I might have mentioned the recent news that the EPA reduced their estimates of methane emissions but now I have even more and better information. This is the information that needs to be reported.
First, the bottom line: Methane levels are way too high–3x normal.
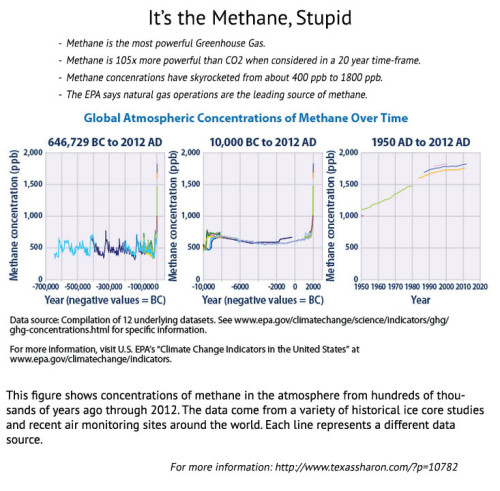
(1) What we know for a fact is that methane concentrations in the atmosphere are skyrocketing.
The EPA has some graphs that show the dramatic spike. Go to this website and then specifically to these figures. At the end of this post are the scientific references the EPA used for this information.
As the charts show, for about 1 million years, methane levels were always between 400 and 800 ppb. Then, all of sudden at the time of the industrial revolution (1850) when we started big time use of fossil fuels, levels of methane (and CO2) started to climb like crazy.
Today concentrations are over 1800 ppb, which means that we have essentially tripled (x3) the average concentration going back a million years.
Whether the leakage rate is 0.1%, 1%, 3%, 10%, doesn’t matter. As an analogy, think about people that are 400 pounds and really obese and suffering from heart disease. Whether they gain another 0.1, 1, 3, or 10 pounds every month moving forward doesn’t matter. Its the wrong question. They need to lose weight, not keep gaining. Translation: we need to stop poking holes in the earth to let the methane out, stop burning fossil fuels, and let nature over time bring the concentration of methane back to the 400 to 800 ppb range.
(2) How much EPA (or EDF, or UT, or NOAA, or UColorado, or anyone else) “estimates” is irrelevant given how much is already in the atmosphere–TOO MUCH. We know how much is actually in the air. 1800 ppb. 3 times what it should be.
(3) There are hundreds of thousands of wells, tanks, pipelines, meters, compressors, pumps, flares, etc, all over Texas, OK, LA, and the gulf that have never been tested for methane leaking. The high majority were installed well before the more modern stuff went in the last 10 years in the shale formations, including in the 1950’s, 60’s, and 70’s. . Methane leakage rates from any piece of equipment vary with time. They will vary with place. They will vary with the operator.
And then there are the brand new facilities like the one in the video below, like the ones all over the Eagle Ford Shale and all over the Barnett Shale that vent the methane. They do it because they can.
(4) The EPA still says natural gas operations are the leading source of methane.
For even more information that was missed in the AP story see Meleah Geertsma’s Blog: EPA Report Confirms Oil and Gas Sector is Among Nation’s Worst Climate Polluters.
To understand methane’s Global Warming Potential (GWP) see: What do leeches have to do with fracking and climate change?
EPA data references.
Spahni, R., J. Chappellaz, T.F. Stocker, L. Loulergue, G. Hausammann, K. Kawamura, J. Flückiger, J. Schwander, D. Raynaud, V. Masson-Delmotte, and J. Jouzel. 2005. Atmospheric methane and nitrous oxide of the late Pleistocene from Antarctic ice cores. Science 310(5752):1317–1321. Accessed May 15, 2007. ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/
Greenland GISP2 ice core: approximately 87,798 BC to 8187 BC
Byrd Station, Antarctica: approximately 85,929 BC to 6748 BC
Greenland GRIP ice core: approximately 46,933 BC to 8129 BC
Blunier, T., and E.J. Brook. 2001. Timing of millenial-scale climate change in Antarctica and Greenland during the last glacial period. Science 291:109–112. Accessed September 13, 2005. ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/
EPICA Dome C, Antarctica: approximately 8945 BC to 1760 AD
Flückiger, J., E. Monnin, B. Stauffer, J. Schwander, T.F. Stocker, J. Chappellaz, D. Raynaud, and J.M. Barnola. 2002. High resolution Holocene N2O ice core record and its relationship with CH4 and CO2. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16(1):10–11. Accessed April 24, 2007.ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/
Law Dome, Antarctica: approximately 1008 AD to 1980 AD
Various Greenland locations: approximately 1075 AD to 1885 AD
Etheridge, D.M., L.P. Steele, R.J. Francey, and R.L. Langenfelds. 2002. Historical CH4 records since about 1000 AD from ice core data. In: Trends: A compendium of data on global change. Oak Ridge, TN: U.S. Department of Energy. Accessed September 13, 2005. http://cdiac.ornl.gov/
Greenland Site J: approximately 1598 AD to 1951 AD
WDCGG (World Data Centre for Greenhouse Gases). 2005. Atmospheric CH4 concentrations for Greenland Site J. Accessed September 1, 2005. http://ds.data.jma.go.
Cape Grim, Australia: 1984 AD to 2010 AD
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). 2011. Monthly mean CH4 concentrations for Cape Grim, Australia. Accessed October 27, 2011. ftp://ftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccg/
Mauna Loa, Hawaii: 1987 AD to 2011 AD
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). 2011. Monthly mean CH4 concentrations for Mauna Loa, Hawaii. Accessed May 10, 2012. ftp://ftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccg/
Steele, L.P., P.B. Krummel, and R.L. Langenfelds. 2002. Atmospheric CH4 concentrations from sites in the CSIRO Atmospheric Research GASLAB air sampling network (October 2002 version). In: Trends: A compendium of data on global change. Oak Ridge, TN: U.S. Department of Energy.http://cdiac.esd.ornl.
About Sharon Wilson
Sharon Wilson is considered a leading citizen expert on the impacts of shale oil and gas extraction. She is the go-to person whether it’s top EPA officials from D.C., national and international news networks, or residents facing the shock of eminent domain and the devastating environmental effects of natural gas development in their backyards.
- Web |
- More Posts(5121)
Excellent reporting. Maybe AP should hire you?
Just another way that natural gas(methane) is increasing our air volume and causing yet unreported climate changes!